Selection Sort ( C & Python 3 )
Selection Sort
Selection sort is conceptually the most simplest sorting algorithm. This algorithm will first find the smallest element in the array and swap it with the element in the first position, then it will find the second smallest element and swap it with the element in the second position, and it will keep on doing this until the entire array is sorted.
It is called selection sort because it repeatedly selects the next-smallest element and swaps it into the right place.
How Selection Sort Works?
Following are the steps involved in selection sort(for sorting a given array in ascending order):
- Starting from the first element, we search the smallest element in the array, and replace it with the element in the first position.
- We then move on to the second position, and look for smallest element present in the subarray, starting from index
1, till the last index. - We replace the element at the second position in the original array, or we can say at the first position in the subarray, with the second smallest element.
- This is repeated, until the array is completely sorted.
Let's consider an array with values
{3, 6, 1, 8, 4, 5}
Below, we have a pictorial representation of how selection sort will sort the given array.
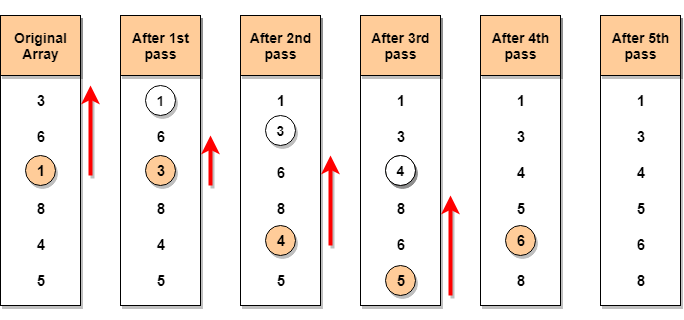 In the first pass, the smallest element will be
In the first pass, the smallest element will be 1, so it will be placed at the first position.
Then leaving the first element, next smallest element will be searched, from the remaining elements. We will get
3 as the smallest, so it will be then placed at the second position.Then leaving 1 and 3(because they are at the correct position), we will search for the next smallest element from the rest of the elements and put it at third position and keep doing this until array is sorted.Example of Selection Sort in C :-
/* Sorting in ascending order using selection sort method in C @uther - Abhishek */ #include <stdio.h> int* selection_sort(int* ,int ); int main() { int n,i,*sorted_array; printf("\nEnter the number of items in the array : "); scanf("%d",&n); int array[n]; for(i=0;i<n;i++) { printf("\nEnter element %d : ",i+1); scanf("%d",&array[i]); } sorted_array=selection_sort(array,n); for(i=0;i<n;i++) { printf(" %d",sorted_array[i]); } return 0; } int* selection_sort(int *array,int n) { int min,swapper,i,j; for(i=0;i<n;i++) { min=array[i]; for(j=i;j<n;j++) { if(min>array[j]) { min=array[j]; array[j]=array[i]; array[i]=min; } } } return array; }
Example of Selection Sort in Python 3 :-
'''
Sorting in ascending order using selection sort in Python 3.
@uther- Abhishek
'''
def selection_sort(array):
for i in range(0,len(array)):
min=array[i]
for j in range(i,len(array)):
if(min>array[j]):
min=array[j];
array[j]=array[i]
array[i]=min
return array
array=list(int(x) for x in input().split())
sorted_array=selection_sort(array)
print(sorted_array)

Comments
Post a Comment