Merge Sort ( C & Python 3 )
Merge Sort
Merge sort is one of the most efficient sorting algorithms. It works on the principle of Divide and Conquer. Merge sort repeatedly breaks down a list into several sublists until each sublist consists of a single element and merging those sublists in a manner that results into a sorted list.
Algorithm:-
Conceptually, a merge sort works as follows :
- Divide the unsorted list into n sublists, each containing 1 element (a list of 1 element is considered sorted).
- Repeatedly merge sublists to produce new sorted sublists until there is only 1 sublist remaining. This will be the sorted list.
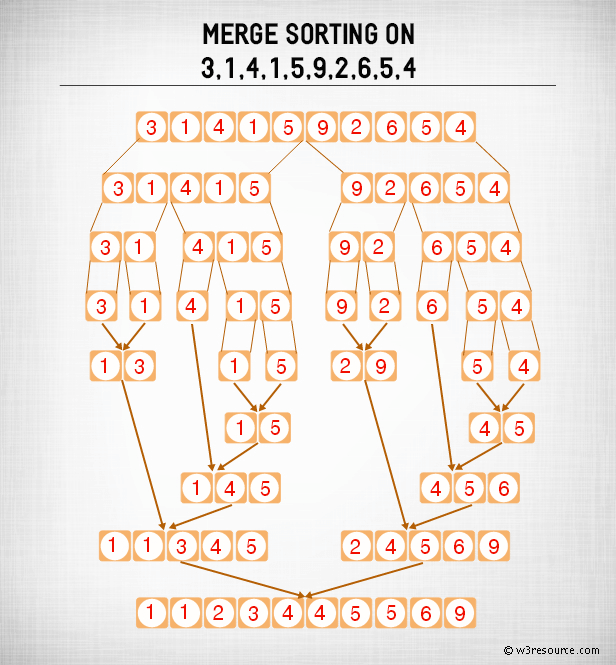
Speed of Merge Sort : -
Best case Scenario : - θ( n log n )
Worst Case Scenario : - θ( n log n )
So, merge sort is one of the most efficient ways of sorting.
The main algorithm of Merging explained with the help of a program in Python 3. ( Not the complete program )
"""
The programming is about taking two sorted list and merging it
into a bigger sorted list.
The backbone of sorting or how merge sort works.
@author: Abhishek
"""
def merging(a,b,m,n):
print("The first sorted list is ",a,m,"\n The second sorted list is ",b,n)
i=j=k=0
c=[]
while(i<m and j<n):
if(a[i]>b[j]):
c.append(b[j])
j=j+1
k=k+1
else:
c.append(a[i])
i=i+1
k=k+1
while(i<m):
c.append(a[i])
i=i+1
while(j<n):
c.append(b[j])
j=j+1
print(c)
a=list(int(x) for x in input("Enter the first list : ").rstrip().split())
b=list(int(x) for x in input("Enter the second list : ").rstrip().split())
a.sort()
b.sort()
merging(a,b,len(a),len(b))
Merge Sort complete program in Python 3"""
Merge Sort Algorithm in Python 3
@author: Abhishek
"""
def merge(array,start,middle,end):
n1=middle-start+1
n2=end-middle
left=[0]*n1
right=[0]*n2
for i in range(0,n1):
left[i]=array[start+i]
for i in range(0,n2):
right[i]=array[middle+1+i]
i=0
j=0
k=start
while(i<n1 and j<n2):
if(left[i]<right[j]):
array[k]=left[i]
i+=1
else:
array[k]=right[j]
j+=1
k+=1
while(j<n2):
array[k]=right[j]
j+=1
k+=1
while(i<n1):
array[k]=left[i]
i+=1
k+=1
def merge_sort(array,start,end):
if(end>start):
middle=(end+start)//2
merge_sort(array,start,middle)
merge_sort(array,middle+1,end)
merge(array,start,middle,end)
array=list(map(int,input("Enter an array : ").split()))
sorted_array=merge_sort(array,0,len(array)-1)
print("The sorted array is ",array)
Output of the Python 3 program
Enter an array : 3 1 4 1 5 9 2 6 5 4
The sorted array is [1, 1, 2, 3, 4, 4, 5, 5, 6, 9]
Merge Sort complete program in C
/*
@uther - Abhishek
Merge Sort in C
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void merge(int* ,int , int ,int );
void merge_sort(int* , int ,int );
int main()
{
int n,i;
printf("\nEnter the number of items to be sorted : ");
scanf("%d",&n);
int array[n];
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
printf("\nEnter the item no %d : ",i+1);
scanf("%d",&array[i]);
}
merge_sort(array,0,n-1);
printf("\nThe Sorted list is as follows :- ");
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
printf("\n\nThe item no %d of the sorted list is : %d",i+1,array[i]);
}
}
void merge_sort(int *array, int start, int end)
{
int middle;
if(start<end)
{
middle=(start+end)/2;
merge_sort(array,start,middle);
merge_sort(array,middle+1,end);
merge(array,start,middle,end);
}
}
void merge(int *array, int start, int middle, int end)
{
int n1,n2;
int i,j,k;
n1=middle-start+1;
n2=end-middle;
int left[n1],right[n2];
for(i=0;i<n1;i++)
{
left[i]=array[start+i];
}
for(j=0;j<n2;j++)
{
right[j]=array[middle+1+j];
}
i=0; j=0; k=start;
while(i<n1 && j<n2)
{
if(left[i]<right[j])
{
array[k]=left[i];
i++;
}
else
{
array[k]=right[j];
j++;
}
k++;
}
while(i<n1)
{
array[k]=left[i];
i++; k++;
}
while(j<n2)
{
array[k]=right[j];
j++; k++;
}
}
Output of the C program
Enter the item no 1 : 3 Enter the item no 2 : 1 Enter the item no 3 : 4 Enter the item no 4 : 1 Enter the item no 5 : 5 Enter the item no 6 : 9 Enter the item no 7 : 2 Enter the item no 8 : 6 Enter the item no 9 : 5 Enter the item no 10 : 4 The Sorted list is as follows :- The item no 1 of the sorted list is : 1 The item no 2 of the sorted list is : 1 The item no 3 of the sorted list is : 2 The item no 4 of the sorted list is : 3 The item no 5 of the sorted list is : 4 The item no 6 of the sorted list is : 4 The item no 7 of the sorted list is : 5 The item no 8 of the sorted list is : 5 The item no 9 of the sorted list is : 6 The item no 10 of the sorted list is : 9
Stay tuned for more updates.

Comments
Post a Comment